
How Wireless Charging Works Explained
Wireless charging can feel like a bit of modern-day magic, but the science behind it is surprisingly simple. It's all about creating an invisible bridge for electricity, letting power flow from a charging pad to your phone without you ever having to plug anything in.
The Invisible Bridge That Powers Your Phone
Think of it like this: an invisible energy bridge is built between the charging pad and your phone using magnetic fields. This whole process relies on a two-part system: the charging pad, which acts as the sender, and your device (your phone, your earbuds, etc.), which is the receiver.
When you set your phone down on the pad, these two get to work. The pad creates a magnetic field, and your phone's internal coil "catches" that field, turning the energy back into electricity to top off your battery. It’s a simple, elegant dance of physics that makes our lives that much easier.
The Two Key Players
To really get what's happening, let's look at the roles of the sender and receiver.
- The Sender (Charging Pad): This is the part you plug into the wall. Inside, it has a coil of wire. When electricity runs through it, the coil creates a magnetic field. This is the starting point of our invisible bridge.
- The Receiver (Your Device): Tucked away inside your phone is a similar, smaller coil. When you bring this receiver coil near the sender's magnetic field, that field creates an electrical current in it, which in turn charges up your battery.
This kind of wireless connection isn't just for our gadgets. The same core idea of reliable, cable-free links is crucial for things like wireless interconnected fire alarms, where seamless communication is a matter of safety.
Believe it or not, this "new" technology has roots stretching back well over a century. The whole concept was kicked off by Nikola Tesla and his wild experiments in the 1890s, where he proved you could send energy through the air. His grand vision for a global wireless power grid never quite happened, but his work laid the foundation for the tech we all use today.
From those early sparks of genius, wireless charging has become a standard feature in billions of devices. It's woven into our daily routines, from the charger on our nightstand to the one built into our car's center console. If you want to explore this topic further, we've got more articles on wireless charging that dive into the details. Grasping these basics will help you make sense of the more advanced concepts we’ll get into next.
Understanding The Science Of Induction
At its heart, wireless charging is just a clever physics trick called electromagnetic induction. It sounds complicated, but the idea is actually pretty simple.
Think of it like this: imagine a spinning jump rope. As it whips around, it creates a small gust of wind. If you hold a tiny pinwheel nearby, that invisible force—the wind—will make the pinwheel spin.
That’s a surprisingly good picture of how wireless charging works. The charging pad is the spinning jump rope, but instead of creating wind, it generates an invisible, pulsing magnetic field. The coil inside your phone is the pinwheel, which “catches” this magnetic energy and turns it back into electricity to juice up your battery.
Creating The Magnetic Field
It all kicks off the moment you plug your charging pad into the wall. This sends a special kind of electricity, called an alternating current (AC), into a tightly wound copper wire inside the pad. Unlike the steady, one-way flow you get from a battery, AC constantly flips its direction.
This rapid back-and-forth movement is the key. As the electricity zips through the wire coil, it generates a magnetic field. And because the electricity is always changing, the magnetic field it creates is also constantly pulsing in and out. This pulsing field is the "wind" in our jump rope analogy, ready and waiting to transfer energy across the gap.
This simple infographic shows the three-step flow of wireless power.
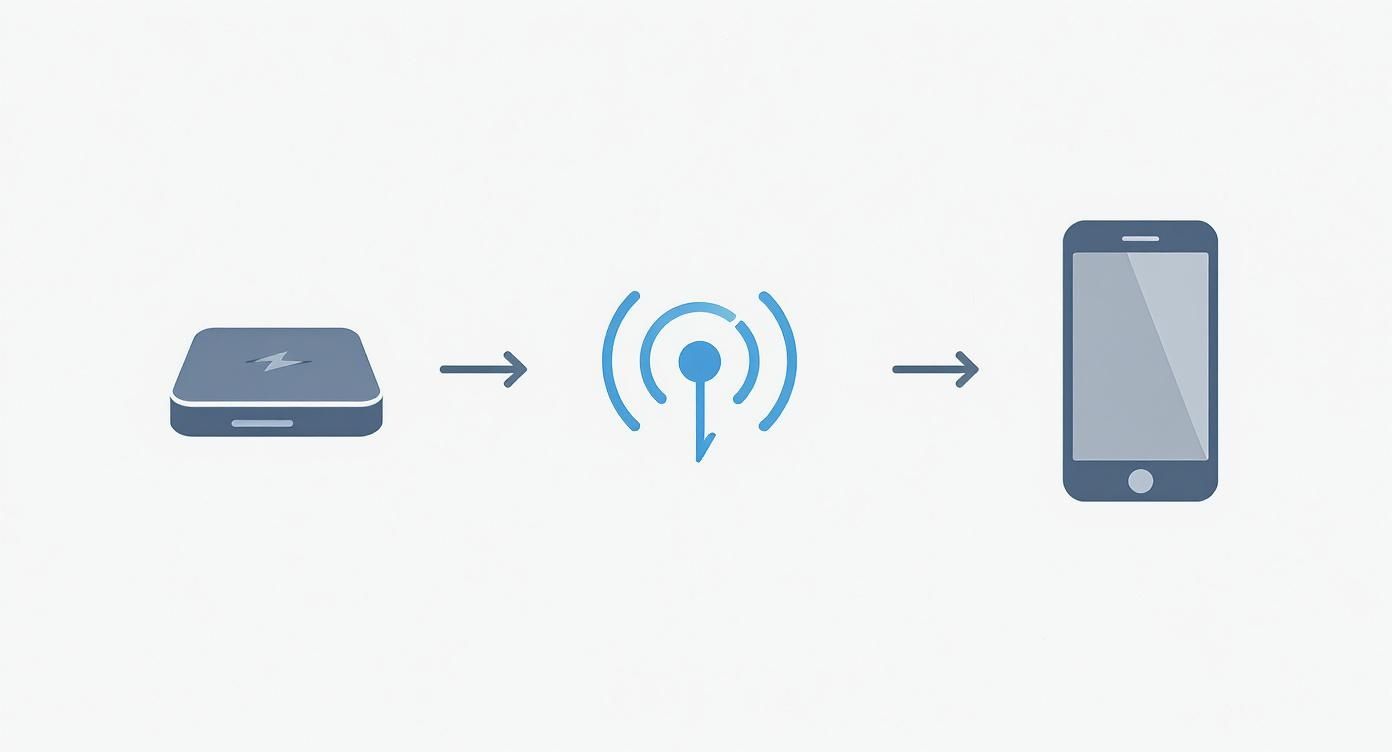
As you can see, the process moves smoothly from the charger, into the magnetic field, and finally to your phone, creating a connection you can't see. This is the basic idea that lets you power up without ever plugging in a cable.
Capturing The Energy
Now for the second half of the magic trick. Tucked away inside your smartphone is another, smaller coil of wire. When you place your phone on the charging pad, this receiver coil enters the magnetic field created by the sender.
The constantly shifting magnetic field then "induces"—or creates—an electrical current in that receiver coil. This happens because the magnetic waves are essentially pushing and pulling the tiny particles within the receiver's copper wire, forcing them to move. That movement is an electrical current.
This brand-new current is then changed into the kind of power your battery needs to store energy. And just like that, the invisible bridge is complete, and your phone starts charging. The whole thing happens without any physical contact, relying entirely on the principles of electromagnetic induction.
Before we move on, let's put wired and wireless charging side-by-side. While both get the job done, they have some pretty clear differences in how they perform.
Wired vs Wireless Charging At a Glance
| Feature | Wired Charging | Wireless Charging |
|---|---|---|
| Convenience | Requires plugging in a physical cable | Just place the device on a pad |
| Speed | Generally faster, especially with fast-charging tech | Typically slower, but improving |
| Efficiency | Highly efficient, little energy lost | Less efficient due to energy lost as heat |
| Wear & Tear | Can cause wear on charging ports over time | Reduces stress on physical ports |
| Clutter | Adds to cable clutter | Creates a cleaner, minimalist setup |
Ultimately, the choice comes down to what you value more—the raw speed and efficiency of a cable or the sheer convenience of just setting your phone down.
The Science Behind The Convenience
The wireless charging we use every day operates on this amazing principle of energy transfer between two coils. An electric current in the charging pad creates a magnetic field, which in turn creates a current in the coil inside your device.
For most phones, this transfer happens over a very short distance, usually less than 10 millimeters. That's why getting the alignment just right is so important. As the tech has gotten better, so have the efficiency and power delivery, with modern phone chargers now ranging from 5W to 15W.
Key Takeaway: The whole process is a two-step energy swap. First, electrical energy in the charging pad is turned into a magnetic field. Then, that magnetic field is turned back into electrical energy inside your phone to charge its battery.
This principle isn't just for our phones, either. The same concept is being used for much bigger jobs, like charging electric vehicles. Digging into the science of optimizing EV charging efficiency shows just how far this technology can go. From the small pad on your desk to the future of transportation, the science of induction is quietly powering our world.
How Coils And Alignment Create The Connection
The real magic behind wireless charging happens inside two simple-looking components: the copper sender and receiver coils. It helps to think of them like a pitcher and catcher in a baseball game. The sender coil in your charging pad is the pitcher, winding up to throw a burst of energy. The receiver coil in your phone is the catcher, and it needs to be in just the right spot to catch it cleanly.
These coils aren't just random loops of wire; their design, shape, and size are engineered with great care. They have to be powerful enough to create a stable magnetic field but also thin and light enough to disappear inside a sleek smartphone without adding any noticeable bulk. It’s a delicate balance that manufacturers are constantly trying to perfect.

This relationship between the two coils is what makes or breaks the whole experience. If they aren't lined up just right, the energy transfer gets sloppy and inefficient—like a wild pitch that sails past the catcher.
Hitting The Sweet Spot
Ever dropped your phone on a wireless charger only to find it’s not actually charging? You probably had to nudge it around a little until you heard that satisfying "ding." That perfect placement is what we call the "sweet spot," and it’s the point where the two coils are most perfectly lined up.
Think about trying to hear someone whispering from across a noisy room. You might catch a word here or there, but most of it is lost. But if they lean in and whisper right into your ear, the message comes through loud and clear.
That’s exactly what’s happening with coil alignment. When the coils are perfectly centered, the magnetic field is strong and focused, which allows for the most efficient power transfer possible. Even a tiny bit of misalignment can weaken the connection, leading to painfully slow charging speeds—or no charging at all.
This is why proper placement is so crucial for how wireless charging works. A solid connection means faster charging and less wasted energy, which also means your phone doesn’t get as warm. This is the whole idea behind technologies like Apple's MagSafe, which uses magnets to snap your device into that perfect position every single time, no guesswork needed.
Improving Flexibility With Resonant Charging
Let's be honest, the need for exact alignment can be a bit of a pain. To solve this, engineers came up with a clever upgrade called resonant charging. This approach adds a bit more wiggle room to the system, making placement less of a headache.
Imagine you have two identical tuning forks. If you strike one, the other will start to vibrate on its own, even from a short distance away, because they share the same natural frequency. Resonant charging works on a very similar principle.
- Tuned Coils: The sender and receiver coils are both "tuned" to vibrate at the same special frequency.
- Stronger Connection: This shared frequency creates a much stronger, more focused magnetic link between them.
- Greater Distance: Because the connection is so strong, the coils can be a bit farther apart or slightly off-center and still transfer power effectively.
This technology is what lets you charge your phone through a thicker case and gives you more freedom when you toss it on the pad. While standard wireless charging requires the coils to be almost touching (usually within a few millimeters), resonant charging can bridge a slightly larger gap.
The Engineering Behind The Coils
The coils themselves are tiny marvels of engineering. They’re typically made from tightly wound, high-quality copper wire to get the best possible connection. Everything from the number of windings and the wire's thickness to the coil's diameter is carefully calculated to optimize performance for a specific device.
For example, a charger built to deliver 15W of power will have a much more powerful coil design than a simple 5W charger meant for your wireless earbuds. Engineers also add a layer of special material behind the coils. This acts like a magnetic shield, directing the field upwards toward the receiver coil in your phone and preventing it from messing with the other sensitive electronics inside. It’s a focused approach that’s essential for both efficiency and safety, making sure the power goes exactly where it's supposed to.
The Qi Standard And Why It Matters
For any wireless charger to work with any phone, they need to speak the same language. That’s where the Qi (pronounced “chee”) standard comes into play. Think of it as the universal rulebook for wireless charging, a bit like how USB-C is becoming the one-size-fits-all connector for everything from laptops to cameras.
Developed by the Wireless Power Consortium (WPC), Qi ensures that a charger from one brand can safely and efficiently power up a device from a completely different one. This is exactly why you don't need a specific Samsung pad for your Galaxy phone or a Google-branded charger for your Pixel. If both devices have that little Qi logo, they're guaranteed to work together.
It was this universal standard that took wireless charging from a quirky, niche feature to the mainstream technology we now find everywhere.
More Than Just Power
The Qi standard does a lot more than just send electricity through the air. It actually manages a smart "digital handshake" between your phone and the charging pad. This constant communication is what makes the whole process both efficient and incredibly safe.
Before any real power starts flowing, the charger sends out a tiny, low-energy signal to see if a compatible device is nearby. If it senses a Qi-certified phone, it kicks things into gear. But if it detects a stray metal object—like your keys or a coin—it stays completely off to prevent any accidents.
The Qi standard is essentially a smart system that lets the charger and your phone constantly talk to each other. This digital dialogue manages power levels, monitors temperature, and ensures the entire process is as safe and efficient as possible.
This two-way conversation allows the charger to deliver the precise amount of power your phone needs at any given moment. It can increase the power for a quick boost or dial it back as the battery gets full, protecting it from unnecessary stress.
The Evolution Of A Global Standard
Wireless charging really took off after 2011 with the launch of the first Qi-ready smartphones. While the early models were a bit clunky, the technology hit a major turning point in 2017 when Apple included Qi in the iPhone 8 and iPhone X. That move cemented Qi as the undisputed industry standard.
Today, the market is booming, with projections forecasting it to shoot past $15 billion in revenue by 2025. We're seeing it pop up in cars, wearables, and all sorts of smart home gadgets. As the tech has matured, we've seen cool new features become common, like 15W fast charging and even reverse wireless charging, where your phone can act as a charger for another device. You can discover more about the history of wireless charging and its impressive journey.
Key Features Of The Qi Standard
The Qi standard isn't just about convenience; it’s packed with essential safety and performance features that make modern wireless charging so reliable.
- Foreign Object Detection (FOD): This is probably the most critical safety feature. If you accidentally drop a paperclip or a coin on the charger, the pad will detect the metal and immediately cut the power. This prevents the object from heating up to dangerous levels.
- Power Control: The charger and your phone are always communicating to adjust the charging speed. This prevents overcharging and helps manage heat—two things that are vital for keeping your battery healthy in the long run.
- Authentication: The more advanced Qi chargers can even perform a security check to verify that your device is a genuine, certified product. This protects you from counterfeit or poorly made accessories that could potentially damage your phone.
These built-in protections are what make Qi-certified charging a trustworthy and dependable way to power up. Without this universal standard, the wireless charging world would be a confusing mess of incompatible products and serious safety risks.
Wireless Charging Safety And Common Myths
As amazing as wireless charging is, it's totally normal to have a few questions about what’s happening behind the scenes. Is it actually safe? Does it waste a bunch of energy? Let's clear the air and tackle the most common concerns, so you can drop your phone on a charger with complete peace of mind.
One of the first things people notice is that their phone and the charging pad get a little warm. This is directly tied to efficiency. While modern wireless systems are impressively good, they just aren't as efficient as plugging in a good old-fashioned cable.
A typical wired charger can be over 95% efficient, which means almost no energy is lost as heat. Wireless charging, on the other hand, usually lands in the 75-80% efficiency ballpark. That small gap in energy gets converted into heat, and that's why things feel warm. This is completely normal and well within the safe operating temperatures manufacturers design for.

This bit of extra heat is a tiny trade-off for going cable-free. But managing that heat is a big deal for your battery's long-term health, which is why the best chargers are built to keep things cool. For instance, the Chargie Supercooled wireless charger has active cooling built-in, making sure your device stays at a happy temperature the whole time it's charging.
Built-In Safety Protocols
Thankfully, the Qi standard—the universal rulebook for wireless charging—was built from the ground up with safety as a top priority. It's packed with smart features to protect you and your gear. The most important one is Foreign Object Detection (FOD).
FOD is a brilliant safety net that stops the charger from powering up if it senses a metal object that isn't a compatible phone or device. Think about it: what if you accidentally dropped your keys or a coin on the charging pad? Without FOD, the charger's magnetic field would create a current in the metal, causing it to heat up fast and potentially become a fire hazard.
Foreign Object Detection works like a vigilant bouncer. The charger sends out a tiny, low-power pulse to see what's on its surface. If it doesn't get the right digital "handshake" back from a Qi-certified device, it refuses to send any real power. Simple and safe.
And that’s just one of the safeguards. Qi-certified chargers also keep a constant eye on temperature and will automatically cut back power or shut down completely if things get too toasty. This constant two-way chat between the pad and your phone keeps the whole process stable and secure.
Debunking Common Wireless Charging Myths
Like any new tech, a few myths start floating around. Let's separate the facts from the fiction.
-
Myth 1: The magnetic fields are bad for your health.
This is probably the biggest worry, but it’s unfounded. The magnetic fields from Qi chargers are extremely low-power and are not the harmful kind of radiation. The field is also incredibly short-range, extending just a few millimeters from the charger. Global regulators have strict safety standards, and Qi chargers operate far below these limits. -
Myth 2: You can’t use your phone while it’s charging wirelessly.
Completely false. It’s perfectly safe to use your phone while it’s sitting on a wireless charger. The only real drawback is that you can’t pick it up and walk around like you could with a long cable. But for checking notifications, watching a video, or taking a hands-free call, there's zero risk. -
Myth 3: Wireless charging wears out your battery faster.
This one has a grain of truth to it, but it’s not the whole story. The real villain for battery longevity isn't wireless charging itself—it's excessive heat and keeping the battery at 100% charge for hours on end. Because wireless charging can generate a bit more heat, a cheap, poorly designed charger could contribute to faster battery aging.The solution? Use a high-quality, Qi-certified charger that's designed to manage heat properly. Avoid those generic, uncertified pads and practice smart charging habits, like not letting your phone cook on the charger long after it's full. This is exactly where smart charging systems become invaluable, gently topping up your battery without stressing it out.
Got Questions? We've Got Answers
Even after getting the basics down, you probably have a few more questions about how wireless charging fits into your day-to-day life. That's totally normal. Let's tackle some of the most common ones and clear up any confusion.
Think of this as the practical side of the story—from charging speeds to whether your favorite phone case will work.
Is Wireless Charging Slower Than Using A Cable?
Okay, let's be straight about this: yes, generally speaking, wireless charging is a little bit slower than plugging in a cable. A direct wired connection is just a more straightforward way to get power into your battery, which is why those super-fast wall adapters can pump out so much power.
But the story doesn't end there. The gap is shrinking fast. Modern wireless chargers, especially those built on the latest Qi standards, can push up to 15W of power. That’s plenty quick for most situations. For most of us, the tiny bit of extra time is a fantastic trade-off for the sheer convenience of just dropping your phone on a pad overnight or at your desk.
Can Any Phone Be Charged Wirelessly?
Nope, not every phone is built for it. For wireless charging to work its magic, the phone needs to have a special receiver coil built right into it by the manufacturer. You can't just add it later.
The good news? This feature is now pretty standard on most new flagship and even mid-range smartphones. If you’ve bought a phone in the last few years, chances are it’s ready to go. If you're not sure, a quick search for your phone model's specs will tell you if it's "Qi-compatible." For some older phones, you might even find special cases that add the capability after the fact.
The easiest way to know for sure? Look for the Qi logo on your phone's box or in its manual. That little symbol is the universal sign that your phone is ready to ditch the cable.
Does My Phone Case Get In The Way?
Most of the time, you're in the clear. Standard plastic, silicone, or thin leather cases—anything under 3-5 millimeters thick—usually won't cause any issues. The magnetic field is strong enough to pass right through without much power loss.
You might hit a snag, however, with a few specific types of cases:
- Super thick, rugged cases: Those heavy-duty, armor-like cases can sometimes create too much of a gap between the charging pad and your phone's internal coil.
- Cases with metal bits: Any metal plates (like the ones for magnetic car mounts) or even metallic decorations will absolutely block the magnetic field and stop the charging process cold.
- Wallet cases with credit cards: This is a big one. It's a really bad idea to sandwich your credit cards between your phone and the charger. The magnetic field could scramble their magnetic strips and leave you with a useless piece of plastic.
Just pop off those kinds of cases or remove any attachments before you set your phone down. It’s the best way to guarantee a safe and efficient charge.
Is It Okay To Leave My Phone On The Charger All Night?
This is the question we hear all the time, and the answer isn't a simple yes or no. Modern phones are smart enough to stop charging once they hit 100%, so you don't have to worry about "overcharging" in the old sense.
The real issue is stress. Keeping a battery pinned at 100% charge for hours, especially while it’s still warm from charging, accelerates its aging process. It's like holding a muscle in a tense position all night long. This is where smart charging habits come into play. A much better approach is to use a system that manages the charge for you, so the battery isn't stuck in that high-stress, fully-charged state.
The sweet spot for battery health is keeping it between 20% and 80% as much as possible. This one simple habit can dramatically extend your battery's lifespan, saving you from the headache and cost of a replacement down the road.
If you want to take control of your battery's health for the long haul, Chargie is a smart hardware and app system that automatically manages your charging. It stops your phone from sitting at 100% all night, which massively reduces battery stress and helps it last for years. Learn more and get your Chargie today.

