Battery Degradation: Impact of Temperature and Charging Rates on Lithium-Ion Cell
Lithium-ion batteries, the cornerstone of modern mobile devices and electric vehicles (EVs), are subject to a variety of factors that influence their lifespan. Among these, temperature and charging rates play a pivotal role in determining how quickly a battery degrades. Understanding these factors is essential for optimizing battery life and ensuring the longevity of devices powered by these batteries.
Read more about battery degradation in this comprehensive study.
The Role of Temperature in Battery Degradation
Temperature has a significant impact on the rate at which lithium-ion batteries degrade. Higher temperatures accelerate the chemical reactions inside the battery, leading to faster degradation. As shown in the chart below, the remaining capacity of a battery decreases significantly as the temperature increases, particularly after multiple charge cycles.
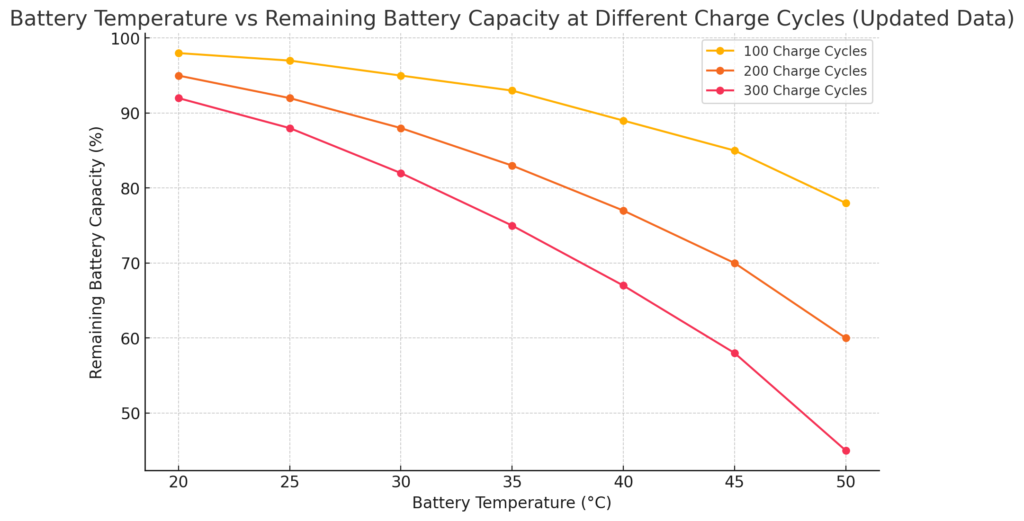
In a real-world scenario, batteries exposed to temperatures as high as 45°C (113°F) can experience more than double the degradation compared to those kept at 25°C (77°F). For instance, after 200 charge cycles, a battery at 45°C may lose around 6.7% of its capacity, compared to only 3.3% at 25°C. This accelerated degradation is due to the growth of the solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer and lithium plating, which reduce the battery’s effective capacity.
The Impact of C-Rate on Battery Longevity
Charging speed, measured in C-rates, is another critical factor in battery degradation. The C-rate indicates how quickly a battery is charged relative to its capacity. Higher C-rates lead to increased stress on the battery’s internal components, accelerating degradation, especially when coupled with high temperatures.
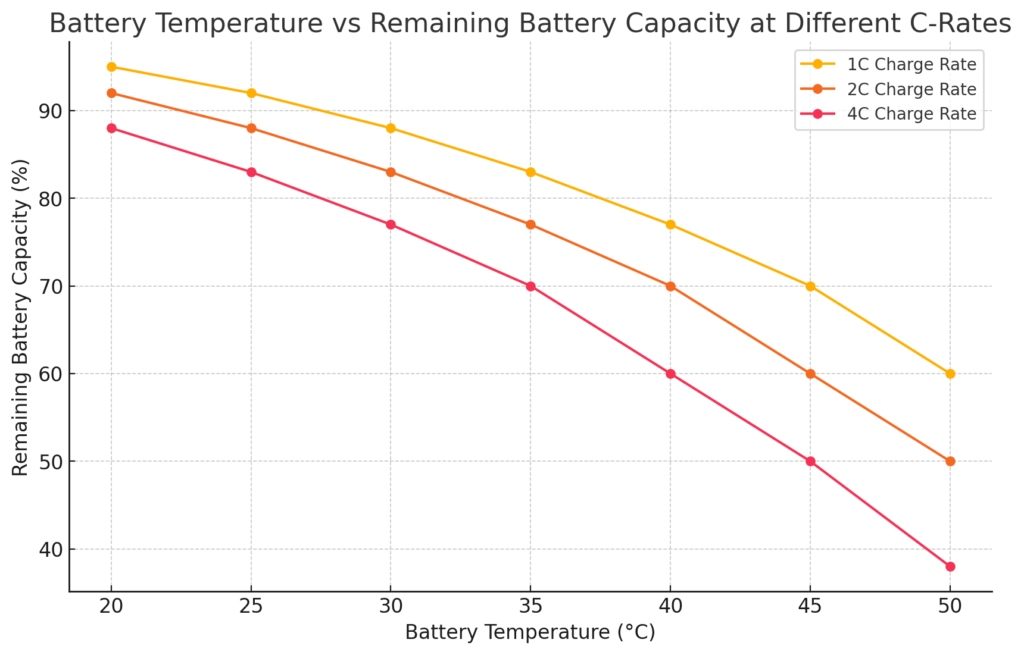
At a 1C charge rate, the degradation is moderate, but as the C-rate increases to 2C and 4C, the remaining capacity drops sharply. For example, at 4C, the capacity loss is significantly greater, particularly at higher temperatures. This highlights the importance of managing both charging speed and temperature to preserve battery health.
The Detrimental Effect of Wireless Charging
Wireless charging, while convenient, can exacerbate battery degradation due to the heat it generates. Unlike wired charging, where heat dissipation is more efficient, wireless charging induces more heat in the battery, increasing the risk of thermal damage. This heat can accelerate the same degradation processes seen with high temperatures and high C-rates, leading to a shortened battery lifespan.
To mitigate these effects, it is recommended to use wireless chargers equipped with thermoelectric coolers. These coolers help manage the temperature during charging, reducing the thermal stress on the battery and thereby extending its life.
Mitigating Battery Degradation with Smart Charging Solutions
Given the detrimental effects of high temperatures and fast charging on battery life, products like Chargie offer an effective solution. Chargie is a charging limiter designed for phones and laptops that mitigates the effects of temperature and high charging rates by:
- Limiting Charging Speed: By throttling the charging speed, Chargie reduces the stress on the battery, particularly at higher temperatures.
- Stopping the Charge Earlier: Instead of charging to 100%, Chargie allows users to set a lower maximum charge percentage, which can significantly extend battery life.
- Temperature Control: Chargie also monitors and limits the maximum battery temperature, preventing overheating and the associated accelerated degradation.
By using such smart charging solutions, users can significantly prolong the life of their devices, ensuring that their batteries maintain a higher capacity for a longer period.
Conclusion
Temperature and charging rates are two of the most significant factors influencing the lifespan of lithium-ion batteries. Managing these factors is crucial for maintaining battery health and extending the useful life of devices. Products like Chargie provide a practical solution by limiting charging speeds, reducing maximum charge levels, and controlling temperature, thereby mitigating the adverse effects of heat and high C-rates on battery degradation. Additionally, when using wireless chargers, opting for those with thermoelectric coolers can further protect your battery from heat-induced damage, helping to maintain its capacity and overall performance

